We review the most important electroclinical aspects and possible subsyndromes of Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy , as well as its genetic background, its pathophysiological and neuroimaging correlates, and treatment. The prevalence of JME in large cohorts has been estimated to be 5% to 10% of all epilepsies and around 18% of idiopathic generalized epilepsies but may be lower in some settings. Today JME is a widely recognized electroclinical idiopathic generalized epilepsy syndrome. The most typical ictal phenomenon is bilateral myoclonia without loss of consciousness. Most patients also present with generalized tonic-clonic seizures , and some with absence seizures. The typical circumstance at diagnosis is a first GTCS episode, after the patient has had myoclonia in the morning.
Typically seizure episodes occur after awakening from a sleep period or in the evening relaxation period and are facilitated by sleep deprivation and sudden arousal. Diagnosis of JME can be made with the history of myoclonus plus a single GTCS plus generalized polyspike-waves or fast spike-waves on the EEG. The prevalence rate of photosensitivity in patients with JME ranges from 8 to 90%.
Hyperventilation can induce absence seizures in patients with JME, while cognitive tasks are efficient in precipitating myoclonic seizures. Most patients have a good prognosis when treated with appropriate drugs, but with a well-known tendency to relapse after withdrawal. However, around 17% are able to discontinue medication and remain seizure-free thereafter.
There is a small but still considerable subgroup of JME patients whose seizures are difficult to treat. Recent findings suggest that patients with JME have worse social adjustment in relevant aspects of their lives, works and familiar relationship. Differential diagnoses include the adolescent-onset progressive myoclonus epilepsies, or other forms of idiopathic generalized epilepsies of adolescence.
The clinical presentation of myoclonic status epilepticus varies widely and depends on its etiology. The location, synchrony, and amplitude of the myoclonic jerks as well as the associated EEG patterns may also differ between the various forms of myoclonic status epilepticus but are less useful diagnostically. The various clinical presentations of myoclonic status epilepticus are described below by etiology and summarized in the following diagrams. The Gastaut classification of each subtype is listed in parentheses. Aggravation of idiopathic generalized epilepsy syndromes by inappropriate antiepileptic drugs is increasingly recognized as a serious and common problem.
Precipitation of status epilepticus by inappropriate medication has rarely been reported. We retrospectively studied all adult patients with IGE taking at least one potentially aggravating AED, who developed video-EEG documented SE over 8 years, and whose long-term outcome was favourable after adjustment of medication. We identified 14 patients aged 15–46 years with a mean duration of epilepsy of 16.4 years. Video-EEG demonstrated typical absence SE in five, atypical ASE in five, atypical myoclonic SE in three and typical MSE in one. Epilepsy had been misclassified as cryptogenic partial in eight cases and cryptogenic generalized in four. The correct diagnosis proved to be juvenile absence epilepsy in six patients, juvenile myoclonic epilepsy in four, epilepsy with grand mal on awakening in two and childhood absence epilepsy in two.
All patients had been treated with carbamazepine and had experienced seizure aggravation or new seizure types before referral. Seven patients had polytherapy with phenytoin , vigabatrin or gabapentin . Potential precipitating factors included dose increase of CBZ or of CBZ and PHT; initiation of CBZ, VGB or GBP; and decrease of phenobarbital. Withdrawal of the aggravating agents and adjustment of medication resulted in full seizure control.
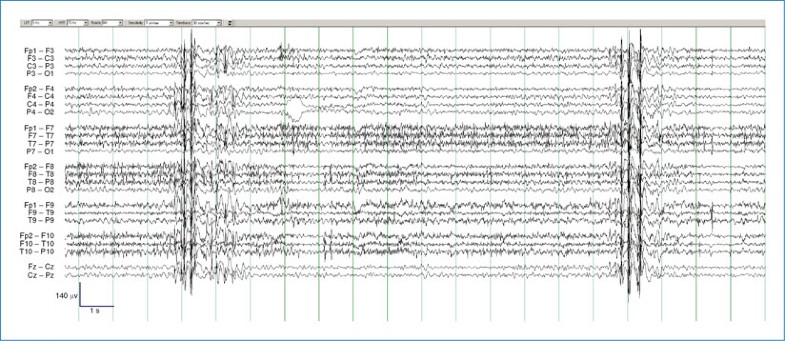
This series shows that severe pharmacodynamic aggravation of seizures in IGE may result in ASE or MSE, often with atypical features. Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy is a clinically heterogenous, generalized epilepsy syndrome with peri-pubertal onset. Myoclonic seizure is the defining seizure type of the syndrome and other seizure types include generalized tonic-clonic seizures and absences. Photosensitivity, eye closure sensitivity, orofacial reflex myoclonia, and praxis induction are the typical epileptic traits of JME. The diagnostic electroencephalogram findings include normal background activity with generalized 3–6 Hz spike-waves with frontal predominance. Treatment response to valproate is generally good.1 Status epilepticus is rarely reported in patients with JME.
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy is one of the most common age-related idiopathic generalized epileptic syndromes. JME may manifest with different seizure types, the most common being myoclonic jerks. Genetic or idiopathic generalized epilepsies account for 15–20% of all epilepsies. These syndromes have always been considered as good prognosis forms of epilepsy over time; however, for some patients, there is a need to maintain antiseizure drugs for a long-time. Lifestyle remains essential and is an integral part of the treatment.
Comorbidities such as obstructive sleep apnea syndrome must be considered and treated. A highly underestimated condition is the risk of sudden unexpected death in epilepsy . Very few data are available about the prevalence of SUDEP in IGE, but patients with generalized tonic-clonic seizures are exposed to this risk. IGEs are also characterized by a specific pharmalogical sensisitivity but may be aggravated by ASDs. Historically, the treatment of IGEs has relied mostly on valproate but this drug should be avoided in women of childbearing potential.
Women with IGE not treated with valproate are more likely to have unsatisfactory seizure control. Female gender appears now as a new risk factor for drug-resistance. Finally, aside from the typical forms, there are epilepsies that fulfill most of the criteria of IGE, but that have an unusual history with GTCS, absences, falls, and drug resistance. Patients do not have psychomotor regression, brain magnetic resonance imaging is normal.
These patients with refractory generalized epilepsy with sleep-related fast activities do not belong to a well-established syndromic category. These cases are considered "intermediary" between IGE and epileptic encephalopathies. Withdrawal of antiepileptic medications, sleep deprivation, or treatment with narrow-spectrum antiepileptic drugs such as phenytoin or carbamazepine can rarely precipitate myoclonic status epilepticus in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Clinically, these patients present with large amplitude, shocklike jerks of the trunk and extremities that occur at irregular intervals. Similar to the typical myoclonic jerks experienced by these patients, myoclonic status epilepticus often presents in the morning.
Importantly, these patients have preserved awareness during these events and can often give a history compatible with the diagnosis of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, if this was not previously known. The EEG shows irregular bursts of generalized, bisynchronouspolyspikesandpolyspike-waves at a frequency of 2-5 Hz that precede and are time-locked with the observed myoclonic jerks. The correct diagnosis was made only after he developed MSE with the use of OXC. Aggravation of genetic generalized epilepsy syndromes by inappropriate ASMs has been well documented, particularly with CBZ. He is a misdiagnosed case of JME and precipitation of MSE with the use of OXC established the diagnosis of JME after 36 years of onset of epilepsy. Jeong et al.13 reported two patients diagnosed with JME by first-ever status epilepticus in adult life.
These three patients' cases emphasizes the importance of asking for myoclonic jerks in patients with new-onset GTCS around pubertal age. GTCS is the seizure type for which most patients with JME seek medical attention for the first time. As detailed above, myoclonic status epilepticus is a syndrome that can occur in a variety of pathological states that cause multifocal cortical and/or brainstem excitation.
Myoclonic status epilepticus can also occur in neurodegenerative conditions and is commonly associated with anoxic brain injury. AB - Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy is a frequent idiopathic generalised epilepsy syndrome with typical clinical and EEG features that can usually be controlled by valproate monotherapy. JME may be under-diagnosed or misdiagnosed; in the latter case, it may be mistaken for partial epilepsy. The incorrect diagnosis of JME is likely to result in inappropriate therapy, which may, in turn, worsen the seizures. While a number of studies have documented that carbamazepine aggravates idiopathic generalised epilepsy, few have shown a worsening of symptoms following the administration of oxcarbazepine .
We report the case of a 44-year-old male affected by JME in which the inappropriate use of OXC precipitated a dramatic worsening of myoclonic seizures. In this case, video-EEG monitoring documented myoclonic status epilepticus with positive and negative myoclonus, correlating with repetitive, continuous, rhythmic, generalised polyspike-and-wave discharges. This is the first case of myoclonic status epilepticus induced by OXC in a patient with JME which is clearly documented by video-EEG. A review of the literature with regards to OXC-induced worsening of seizures is also presented. N2 - Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy is a frequent idiopathic generalised epilepsy syndrome with typical clinical and EEG features that can usually be controlled by valproate monotherapy.
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy is a frequent idiopathic generalised epilepsy syndrome with typical clinical and EEG features that can usually be controlled by valproate monotherapy. Myoclonic status epilepticus in patients without epilepsy, or de novo MSE, is a rare condition associated with several acute symptomatic etiologies, including drugs and toxins. We describe a 94-year-old woman with Alzheimer dementia and long use of mirtazapine 30 mg/d and alprazolam 1 mg/d who developed MSE approximately 24 hours after abrupt discontinuation of alprazolam.
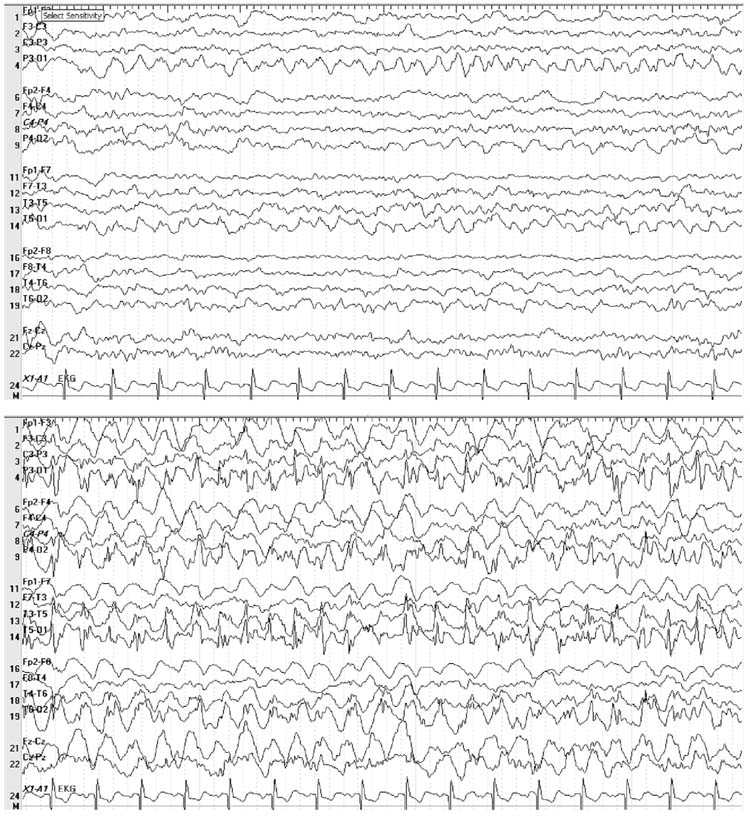
The patient was taking sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim for urinary tract infection, diagnosed 2 weeks before admission. Routine laboratory examinations were normal and head computed tomography showed no acute injuries. Continuous electroencephalogram monitoring revealed very frequent generalized spikes and polyspikes in a markedly slowed background activity. Intravenous VPA 500 mg thrice a day and alprazolam 0.5 mg twice a day were prescribed, and antibiotic was switched to piperacillin/tazobactam. Myoclonic jerks ceased completely and electroencephalogram showed no epileptiform discharges 2 days after VPA treatment onset, with recovery of baseline neurological status.
This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first report of de novo MSE related to abrupt discontinuation of benzodiazepines. Seizures and status epilepticus are potential adverse events after abrupt withdrawal of chronically used benzodiazepines, especially in conditions with intrinsic epileptogenic susceptibility, such as Alzheimer disease. Many patients remain comatose after successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation due to brain damage caused by hypoxemia. Acute posthypoxic myoclonus occurs in about 19-37% of these patients, typically within the first 24 hours after CPR, but knowledge about this illness is limited . Acute PHM can be divided into status myoclonus and focal myoclonus. In daily practice different terms are used for status myoclonus, e.g. generalized myoclonus, myoclonus status, or myoclonic status epilepticus .
Wijdicks et al. defined status myoclonus as spontaneous or sound-sensitive, repetitive, irregular brief jerks in both face and limb present during most of the first day after CPR . Focal myoclonus, such as platysmal myoclonus has also been reported in patients after CPR . Most studies concerning acute PHM were performed before treatment with hypothermia after CPR was implemented.
Nowadays, acute PHM is often suppressed during the first day after admission by the administration of sedative drugs or neuromuscular blocking agents during hypothermia treatment. Stimulus sensitive myoclonus often interferes with nursing of these patients, is deterrent to relatives, and is difficult to treat. Lance-Adams syndrome, chronic PHM, also occurs in patients after CPR, but usually arises in the post-intensive care unit period and it is mainly seen after hypoxia as primary cause of CPR . Typical absence status epilepticus occurs in about one third of patients with typical absence seizures. As such, it is a common occurrence in patients who suffer from the idiopathic generalized epilepsy syndromes such as childhood absence epilepsy , juvenile absence epilepsy , and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy .
Clinically, the seizures may divide into simple and complex subtypes. Dravet syndrome develops during early childhood; it has focal and generalized components (and thus is not clearly a type of generalized-onset or focal-onset seizure). Fever-induced focal seizures predominate during the first year of life; at about age 2 years, seizures evolve into generalized myoclonic seizures.
Generalized myoclonic seizures are characterized by frequent axial-predominant bilateral myoclonic jerks that are accompanied by bursts of bisynchronous spike and wave activity on EEG. Other seizure types that can occur in Dravet syndrome include atypical absence, clonic, atonic, and tonic-clonic seizures. Psychomotor development stagnates or regresses during the second year of life. Mutations in the sodium channel alpha-1 subunit gene occur in 70 to 80% of patients with Dravet syndrome.
The ictal EEG of acute postanoxic myoclonus has been reported to manifest in various patterns. This suggests that various mechanisms for postanoxic myoclonus status epilepticus may be involved,789 which may also be a result of differences in location and degree of anoxic injury. Status epilepticus is an increasingly recognized public health problem in the United States. Status epilepticus is associated with a high mortality rate that is largely contingent on the duration of the condition before initial treatment, the etiology of the condition, and the age of the patient. Three new preparations—fosphenytoin, rectal diazepam, and parenteral valproate—have implications for the management of status epilepticus. However, randomized controlled trials show that benzodiazepines should be the initial drug therapy in patients with status epilepticus.
Despite the paucity of clinical trials comparing medication regimens for acute seizures, there is broad consensus that immediate diagnosis and treatment are necessary to reduce the morbidity and mortality of this condition. Moreover, investigators have reported that status epilepticus often is not considered in patients with altered consciousness in the intensive care setting. In patients with persistent alteration of consciousness for which there is no clear etiology, physicians should be more quickly prepared to obtain electroencephalography to identify status epilepticus.
Physicians should rely on a standardized protocol for management of status epilepticus to improve care for this neurologic emergency. These patients usually have some degree of baseline cognitive impairment and suffer from other seizure types such as myoclonic, tonic, and atonic seizures in addition to the atypical absence seizures. The seizures manifest with some degree of impaired consciousness, which may be difficult to detect due to an already abnormal baseline cognition.
In patients with one of the progressive myoclonic epilepsy syndromes, the clinical myoclonus is often also small amplitude, multifocal, asymmetric, and asynchronous. Notably, particularly early in the disease course, the myoclonus may exhibit a reflex component whereby it is exacerbated by action or stimulation. However, unlike myoclonic status epilepticus associated with the symptomatic generalized epilepsies, mental status is not depressed as a result of the myoclonic status epilepticus.
Again, this may be difficult to tease out due to the concomitant cognitive decline related to the underlying pathophysiology of these diseases. The EEG in these cases typically shows mild to moderate background slowing, with multifocal or generalized spikes and polyspike-waves that variably correlate with the clinical jerks. Seizures that originate from a specific cortical focus are usually sequelae of focal brain dysfunction or injury. When the underlying cause of such focal dysfunction is apparent the seizure is considered symptomatic of this lesion.
If no associated focal lesion is identified despite the footprint of a focal onset, either clinically or on EEG, the etiology is termed cryptogenic. The outcome of treatment for myoclonic status epilepticus depends on the underlying etiology. Myoclonic status epilepticus in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy and other idiopathic generalized epilepsy syndromes is usually very responsive to benzodiazepines and other broad-spectrum antiepileptic medications. Myoclonic status epilepticus that occurs in developmental and epileptic encephalopathies is more indolent, chronic, and difficult to treat. Myoclonic status epilepticus in neurodegenerative disorders is often a late occurrence and can be difficult to treat and can be associated with a poor outcome.
In contrast, if myoclonic status epilepticus is due to a reversible toxic-metabolic cause, outcome can be good with the correction of the metabolic insult or removal of the offending agent. Myoclonic status may be associated with a wide range of etiologies, including anoxic brain injury, toxic-metabolic encephalopathies, and exacerbations of certain epilepsy syndromes. The clinical presentation and significance of frequent myoclonic jerks differs greatly by etiology.























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.